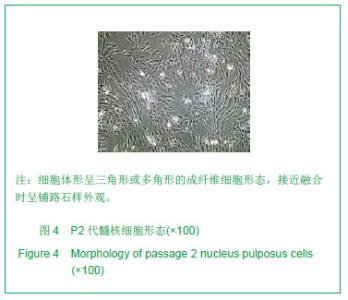
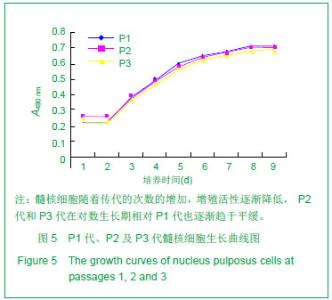
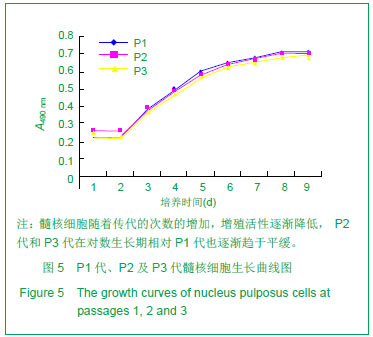
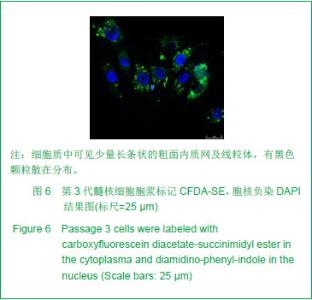
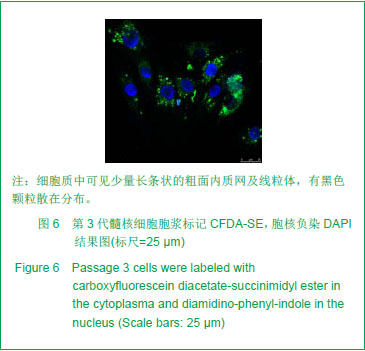
| [1]Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Martin BI. Back pain prevalence and visit rates: estimates from U.S. national surveys, 2002. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(23):2724-2727.[2]Katz JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88 (Suppl 2):21-24.[3]Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20(11): 1307-1314.[4]孟壮志, 朱青安, 范真,等. 腰骶部椎间盘髓核摘除对脊柱稳定性影响的生物力学研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志. 1999; 17 (1): 75-76.[5]王海, 熊承杰, 黄博, 等. 椎间盘组织工程学种子细胞来源的研究进展[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志. 2012; 22(1):77-81.[6]Clouet J, Vinatier C, Merceron C, et al. The intervertebral disc: from pathophysiology to tissue engineering. Joint Bone Spine. 2009; 76(6):614-618.[7]Anisimov SV. Cell therapy in treating age-related intervertebral disc pathology. Adv Gerontol. 2012; 25(1):105-111.[8]Chan SC, Gantenbein-Ritter B. Intervertebral disc regeneration or repair with biomaterials and stem cell therapy--feasible or fiction? Swiss Med Wkly. 2012; 142: w13598.[9]Drazin D, Rosner J, Avalos P, et al. Stem cell therapy for degenerative disc disease. Adv Orthop. 2012; 2012:961052.[10]Hohaus C, Ganey TM, Minkus Y, et al. Cell transplantation in lumbar spine disc degeneration disease. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17 Suppl 4:492-503.[11]Blagodatskii MD, Solodun Iu V, Treshchuk LI. Reactive-inflammatory process in the spinal canal after implantation of autologous intervertebral disk cartilage. Arkh Patol. 1987; 49(1):26-31.[12]Brisby H, Tao H, Ma DD, et al. Cell therapy for disc degeneration-potentials and pitfalls. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35(1):85-93.[13]Munnich U, Heyll U. Autologous intervertebral disc cell transplantation. Versicherungsmedizin. 2007; 59(2):98-99.[14]Kayama S, Olmarker K, Larsson K, et al. Cultured, autologous nucleus pulposus cells induce functional changes in spinal nerve roots. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23(20): 2155-2158.[15]Meisel HJ, Siodla V, Ganey T, et al. Clinical experience in cell-based therapeutics: disc chondrocyte transplantation A treatment for degenerated or damaged intervertebral disc. Biomol Eng. 2007; 24(1):5-21.[16]Katz JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88 Suppl 2(4):21-4.[17]Atlas SJ, Nardin RA. Evaluation and treatment of low back pain: an evidence-based approach to clinical care. Muscle Nerve. 2003; 27(3):265-284.[18]候树勋, 彭宝淦. 椎间盘退变性疾病研究现状与展望. 中国临床康复. 2012; 6(14):2096-2097.[19]Devereaux M. Low back pain. Med Clin North Am. 2009; 93(2):477-501.[20]Evans C. Potential biologic therapies for the intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88 Suppl 2:95-98.[21]海涌. 生物治疗在退变性椎间盘疾病治疗中的作用. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志. 2004; 14(6):373.[22]李高峰,张绍昆,付长峰,等.细胞因子及基因治疗椎间盘退行性变的研究动态.中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2009; 13 (2) :359-362.[23]徐远, 俞兴, 徐林. 细胞移植治疗椎间盘退变研究进展. 生物骨科材料与临床研究. 2011; 8(1):30-33.[24]张海龙, 侯铁胜. 细胞移植治疗椎间盘退变的研究进展. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志. 2007; 17(3):226-228.[25]戴刚,李起鸿,周强,等. 关节软骨组织工程种子细胞的优化获取. 第三军医大学学报. 2002; 24(2):129-131.[26]周红星, 杨柳, 李起鸿. 骨组织工程研究中种子细胞、支架材料及其相互关系. 中国临床康复. 2004; 8(14):2706-2707.[27]Risbud MV, Guttapalli A, Tsai TT, et al. Evidence for skeletal progenitor cells in the degenerate human intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32(23):2537-2544.[28]Blanco JF, Graciani IF, Sanchez-Guijo FM, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stromal cells from human degenerated nucleus pulposus: comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells from the same subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010; 35(26):2259-2265.[29]Feng G, Yang X, Shang H, et al. Multipotential differentiation of human anulus fibrosus cells: an in vitro study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(3):675-685.[30]Huang B, Liu LT, Li CQ, et al. Study to determine the presence of progenitor cells in the degenerated human cartilage endplates. Eur Spine J. 2012; 21(4):613-622.[31]Brisby H, Tao H, Ma DD, et al. Cell therapy for disc degeneration--potentials and pitfalls. Orthop Clin North Am. 2004; 35(1):85-93.[32]Orozco L, Soler R, Morera C, et al. Intervertebral disc repair by autologous mesenchymal bone marrow cells: a pilot study. Transplantation.2011; 92(7):822-828.[33]Sakai D, Mochida J, Iwashina T, et al. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells transplanted to a rabbit degenerative disc model: potential and limitations for stem cell therapy in disc regeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(21):2379-2387.[34]徐远,俞兴,徐林.骨髓间充质干细胞与髓核细胞的体外共培养[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011; 15(27):4964- 4968.[35]肖剑, 贾连顺, 程岗,等.兔腰椎间盘髓核细胞活力测定及外源性基因在其中的表达[J].中国临床康复,2002; 6(20):3023-3024.[36]肖剑,赵剑, 潘欣,等.兔腰椎间盘髓核细胞的培养及形态观察[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2001; 8(8):793-794.[37]胡明,马远征,黄凤山,等.成人退变性椎间盘髓核细胞体外培养及形态学观察[J].中国实用骨科杂志,2011; 17(10):902-904[38]陶凤华,李锋,潘峰,等. 改良法原代培养兔髓核细胞及其生物学特性[J]. 华中医学杂志,2008; 32(4):240-241.[39]于占革, 杨威, 温莹, 等. 兔不同节段椎间盘髓核细胞培养特性的比较[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010; 20(8):689-693.[40]张传志, 周跃, 李长青. 兔髓核细胞体外最佳培养条件的探索[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2005; 13(14):1093-1096.[41]王锋,吴小涛, 王运涛. 单纯Ⅱ型胶原酶消化法分离、培养人退变椎间盘髓核细胞的形态学观察[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010; 20(4):300-304. |